 |
Oklahoma Administrative Code (Last Updated: March 11, 2021) |
 |
TITLE 310. Oklahoma State Department of Health |
 |
Chapter 281. Diagnostic X-Ray Systems |
 |
Subchapter 1. General Provisions |
SECTION 310:281-1-2. Definitions
Latest version.
- The following words or terms, when used in this Chapter, shall have the following meaning, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise."Absorbed dose" means the energy imparted to matter by ionizing radiation per unit mass of irradiated material at the place of interest. The special units of absorbed dose are the rad and the gray (Gy). (See definitions of "Rad" and "Gray" in this Section.)"Accessible surface" means the external surface of the enclosure or housing provided by the manufacturer."ACR Standard for Teleradiology" means the degree or level of requirements for the performance of teleradiology to include qualifications of personnel, equipment guidelines, licensing, credentialing, communication, quality control, and quality improvement to serve as a model for all physicians and health care workers who utilize teleradiology."Act" means applicable portions of the Oklahoma Public Health Code. (Title 63 O.S. Supp. 2001, Sections 1-1501.1 et seq.)"Adult" means any individual 18 or more years of age."Aluminum equivalent" means the thickness of type 1100 aluminum alloy affording the same attenuation, under specified conditions, as the material in question. The nominal chemical composition of type 1100 aluminum alloy is 99.00 percent minimum aluminum, 0.12 percent copper."American College of Radiology" (ACR) means the principal organization of radiologists, radiation oncologists, and clinical medical physicists in the United States that is a non-profit professional society whose primary purposes are to advance the science of radiology, improve service to the patient, study socioeconomic aspects of the practice of radiology, and encourage continuing education for radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists, and persons practicing in allied professional fields."Analog signal" means a form information transmission in which the signal varies in a continuous manner and is not limited to discrete steps."Applicator" means a structure which determines the extent of the treatment field at a given distance from the virtual source."Assembler" means any person engaged in the business of assembling, replacing, or installing one or more components into a diagnostic x-ray system or subsystem. The term includes the owner of a diagnostic x-ray system and/or his or her employee or an agent who assembles components into a diagnostic x-ray system that is subsequently used to provide professional or commercial services."Attenuate" means to reduce the exposure rate upon passage of radiation through matter."Attenuation block" means a block or stack, having dimensions 20 centimeters by 20 centimeters by 3.8 centimeters, of type 1100 aluminum alloy or other materials having equivalent attenuation."Automatic exposure control" means a device which automatically controls one or more technique factors in order to obtain at a preselected location(s) a required quantity of radiation. (See also definition of "Phototimer" in this section.)"Average Glandular Dose" means, in mammography, the value in millirad for a given breast or phantom thickness which estimates the average absorbed dose to the glandular tissue extrapolated from free air exposure and based on fixed filter thickness and target material."Barrier" (See definition of "Protective barrier" in this Section.)"Beam axis" means a line from the source through the centers of the x-ray fields."Beam-limiting device" means a device which provides a means to restrict the dimensions of the x-ray field."Beam monitoring system" means a system designed to detect and measure the radiation present in the useful beam."Beam quality" means a term that describes the penetrating power of the x-ray beam. This is identified by half-value layer and is influenced by kilovolt peak (kVp) and filtration."Beam scattering foil" means a foil used in order to scatter a beam of electrons."Board" means the Oklahoma State Board of Health."Bone densitometer" means a system intended for medical purposes to measure bone density and mineral content by x-ray transmission measurements through the bone and adjacent tissues."Calendar quarter" means not less than 12 consecutive weeks nor more than 14 consecutive weeks. The first calendar quarter of each year shall begin in January and subsequent calendar quarters shall be so arranged such that no day is included in more than one calendar quarter and no day in any one year is omitted from inclusion within a calendar quarter. No permittee shall change the method observed by that individual in determining calendar quarters for purposes of these regulations except at the beginning of a calendar year."Calendar year" means the time period running from January 1st through December 31st."Calibration" means the determination of:(A) the response or reading of an instrument relative to a series of known radiation values over the range of the instrument; or(B) the strength of a source of radiation relative to a standard."Central axis of the beam" means a line passing through the virtual source and the center of the plane figure formed by the edge of the first beam limiting device."Cephalometric system" means a system intended for the radiographic visualization and measurement of the dimensions of the human head."Certified components" means components of diagnostic x-ray systems, which are subject to regulations promulgated under the Radiation Control for Health and Safety Act of 1968.(21 CFR Parts 1000-1030.)"Certified system" means any diagnostic x-ray system which has one or more certified component(s)."CFR" means Code of Federal Regulations."Changeable filter" means any filter, exclusive of inherent filtration, which can be removed from the useful beam through any electronic, mechanical, or physical process."Coefficient of variation" (C) means the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean value of a population of observations. It is estimated using the equation set forth in Appendix E."Collimator" means a device or mechanism by which the x-ray beam is restricted in size."Computed tomography" (CT) means the production of a tomogram by the acquisition and computer processing of x-ray transmission data."Computed tomography dose index" (CTDI) means the integral from -7T to +7T of the dose profile along a line perpendicular to the tomographic plane divided by the product of the nominal tomographic section thickness and the number of tomograms produced in a single scan, as set forth in Appendix E."Contrast scale"(CS) means the change in the linear attenuation coefficient per CTN relative to water; as set forth in Appendix E."Control panel" means that part of the radiation machine control upon which are mounted the switches, knobs, push buttons, and other hardware necessary for manually setting the technique factors."Cooling curve" means the graphical relationship between heat units stored and cooling time."CT conditions of operation" means all selectable parameters governing the operation of a CT x-ray system including, but not limited to, nominal tomographic section thickness, filtration, and the technique factors as defined in 310:281-11-15."CT gantry" means the tube housing assemblies, beam limiting devices, detectors and the supporting structures and frames, which hold these components."CT number" (CTN) means the number used to represent the x-ray attenuation associated with each elemental area of the CT image, as set forth in Appendix E."Dead-man switch" means a switch so constructed that a circuit closing contact can be maintained only by continuous pressure on the switch by the operator."Declared pregnant woman" means a woman who has voluntarily informed the permittee, in writing, of her pregnancy and the estimated date of conception. The declaration remains in effect until the declared woman voluntarily withdraws the declaration in writing or is no longer pregnant."Deep dose equivalent"(DDE) (HD) means the dose which applies to external whole-body exposure and is the dose equivalent at a tissue depth of 1 cm (1000 mg/cm2)."Department" means the Oklahoma State Department of Health."Detector" (See definition of "Radiation detector" in this Section.)"Diagnostic source assembly" means the tube housing assembly with a beam-limiting device attached."Diagnostic-type tube housing" means an x-ray tube housing so constructed that the leakage radiation measured at a distance of 1 meter from the source cannot exceed 100 mr in 1 hour when the tube is operated at its maximum continuous rated current for the maximum rated tube potential."Diagnostic x-ray system" means an x-ray system designed for irradiation of any part of the human body for the purpose of diagnosis or visualization.Types of diagnostic x-ray systems are as follows:(A) "Mobile diagnostic x-ray system" means a diagnostic x-ray system mounted on a permanent base with wheels and/or casters for moving while completely assembled.(B) "Portable diagnostic x-ray system" means a diagnostic x-ray system designed to be hand-carried.(C) "Stationary diagnostic x-ray system" means a diagnostic x-ray system which is installed in a fixed location. A diagnostic x-ray system installed in a vehicle designed to be operated on the highway shall be deemed to be a stationary x-ray system."Diaphragm" means a device or mechanism by which the x-ray beam is restricted in size."Direct scattered radiation" means that scattered radiation which has been deviated in direction only by materials irradiated by the useful beam. (See definition of "Scattered radiation" in this Section.)"Dose" means absorbed dose or dose equivalent as appropriate."Dose equivalent"(DE) (HT) means a quantity that expresses on a common scale for all radiation a measure of the postulated effect on a given organ. It is defined as the absorbed dose in rads times certain modifying factors. The units of dose equivalent are the rem and sievert (Sv). (See definitions of "Rem" and "Sievert" in this Section.)"Dose limits" means the permissible upper bounds of radiation doses established in accordance with this Chapter. For the purposes of this Chapter, "limits" is an equivalent term."Dose monitoring system" means a system of devices for the detection, measurement, and display of quantities of radiation."Dose monitor unit" means a unit response from the dose monitoring system from which the absorbed dose can be calculated."Dose profile" means the dose as a function of position along a line."Effective dose equivalent"(EDE) (HE) is the sum of the products of the dose equivalent to the organ or tissue (HT) and the weighting factors (WT) applicable to each of the body organs or tissues that irradiated (HE = Σ WTHT)."Elemental area" means the smallest area within a tomogram for which the x-ray attenuation properties of a body are depicted. (See also definition of "Picture element" in this section.)"Embryo/fetus" means the developing human organism from conception until the time of birth."Entrance exposure" means the exposure, expressed in roentgens, measured in air with the specified technique, calculated or adjusted to represent the exposure at the point where the center of the useful beam enters the patient."Entrance exposure rate" means the exposure per unit time at the point where the center of the useful beam enters the patient."Equipment" (See definition of "X-ray system" in this Section.)"Exposure" means the absolute value of the total charge of the ions of one sign produced in air when all the electrons (negatrons and positrons) liberated by photons in a unit mass volume of air are completely stopped in air. The special unit of exposure is the roentgen. (See definition of "Roentgen" in this Section.)"Exposure rate" means the exposure per unit of time, such as roentgen per minute and milliroentgen per hour."External dose" means that portion of the DE received from any source of radiation outside the body."Extremity" means hand, elbow, arm below the elbow, foot, knee, and leg below the knee. The arm above the elbow and the leg above the knee are considered part of the whole body."Facility" means the location at which one or more diagnostic x-ray systems, subject to these rules, are located and/or installed. Facilities with several such systems located and/or installed in different buildings and/or vehicles, but at the same street address and under the same administrative control will be considered to be one facility."Field emission systems" means systems which uses an x-ray tube in which electron emission from the cathode is due solely to the action of an electric field."Field flattening filter" means a filter used to provide dose uniformity over the area of a useful beam of x-rays at a specified depth."Field size" means the dimensions along the major axes of an area in a plane perpendicular to the central axis of the useful beam of incident radiation at the normal treatment distance and defined by the intersection of the major axes and the 50 percent isodose line. Material shall be placed in the beam such that the dose maximum is produced at the normal treatment distance when the field size is being determined."Filter" means material placed in the useful beam to absorb preferentially selected radiations."Fluoroscopic imaging assembly" means a subsystem in which x-ray photons produce a fluoroscopic image. It includes the image receptor(s) such as the image intensifier and spot-film device, electrical interlocks, if any, and structural material providing linkage between the image receptor and diagnostic source assembly."Focal spot" means the area projected on the anode of the x-ray tube by the electrons accelerated from the cathode and from which the useful beam originates."Fog test" means an evaluation of increased density and reduced contrast on film, which has not been exposed to the radiation field. This is usually done by processing unexposed film and measuring the density."Gantry" means that part of the system supporting and allowing possible movement of the radiation head."General purpose radiographic x-ray system" means any diagnostic x-ray system, which, by design, is not limited to radiographic examination of specific anatomical regions."Gonadal shield" means a protective barrier for the testes or ovaries."Gray" (Gy) means the SI unit of absorbed dose. One gray is equal to an absorbed dose of 1 joule/kilogram (100 rads) of tissue."Half-value layer" (HVL) means the thickness of specified material which attenuates the beam of radiation to an extent such that the exposure rate is reduced to one-half of its original value. In this definition, the contribution of all scattered radiation, other than any which might be present initially in the beam concerned, is deemed to be excluded."Healing arts" means those professional disciplines authorized by the laws of this state to use x-rays in the diagnosis of human or animal disease."Healing arts screening" means the testing of human beings using diagnostic x-ray systems for the detection or evaluation of health indications when such tests are not specifically and individually ordered by a licensed practitioner of the healing arts legally authorized to prescribe such x-ray examinations for the purpose of diagnosis."Heat unit" means a unit of energy equal to the product of the peak kilovoltage, milliamperes, and seconds, i.e., kVp x mA x second."High radiation area" means any area, accessible to individuals, in which there exists radiation at such levels that a major portion of the body could receive in any one hour a dose in excess of 100 millirems."Human use" means the external administration of radiation to human beings."Image intensifier" means a device installed in its housing, which instantaneously converts an x-ray pattern into a corresponding light image of higher energy density."Image receptor" means any device such as a fluorescent screen or radiographic film which transforms incident x-ray photons either into a visible image or into another form which can be made into a visible image by further transformations."Image receptor support" means for mammographic systems that part of the system designed to support the image receptor in a horizontal plane during a mammographic examination."Inherent filtration" means the filtration of the useful beam provided by the permanently installed components of the tube housing assembly."Inspection" means an official examination or observation including, but not limited to, records, tests, surveys, and monitoring to determine compliance with rules, regulations, orders, requirements, and conditions of the Department."Interlock" means:(A) a device arranged or connected such that the occurrence of an event or condition is required before a second event or condition can occur or continue to occur; or(B) a device for precluding access to an area of high radiation by automatically reducing the exposure rate."Interruption of radiation" means the stopping of irradiation with the possibility of continuing irradiation without resetting of operating conditions at the control panel."Irradiation" means the exposure of matter to ionizing radiation."Isocenter" means the intersection of the collimator axis of rotation and the gantry axis of rotation."Kilovolts peak (kVp)" means the maximum value of the potential difference across the x-ray tube during an exposure and shall be deemed to be equivalent to kilovolts peak (kVp)."kV" means kilovolts."kWs" means kilowatt second. It is equivalent to 10 (kV) x (mA) x (s), i.e., as set forth in Appendix E."Lead equivalent" means the thickness of lead affording the same attenuation, under specified conditions, as the material in question."Leakage radiation" means radiation emanating from the diagnostic source assembly except for:(A) the useful beam, and(B) radiation produced when the exposure switch or timer is not activated."Leakage technique factors" means the technique factors associated with the diagnostic assembly, which are used in measuring leakage radiation. The technique factor(s) are defined as follows:(A) For diagnostic source assemblies intended for capacitor energy storage equipment, it is the maximum-rated peak tube potential and the maximum-rated number of exposures in an hour for operation at the maximum-rated peak tube potential with the quantity of charge per exposure being 10 millicoulombs, i.e., 10 milliampere seconds, or the minimum obtainable from the unit, whichever is larger.(B) For diagnostic source assemblies intended for field emission equipment rated for pulsed operation, it is the maximum-rated peak tube potential and the maximum-rated number of x-ray pulses in an hour for operation at the maximum-rated peak tube potential.(C) For all other diagnostic source assemblies, it is the maximum-rated peak tube potential and the maximum-rated continuous tube current for the maximum-rated peak tube potential."Lens dose equivalent (LDE)" means the external DE to thelens of the eye at a tissue depth pf 0.3 cm (300 mg/cm2)."Light field" means that area of the intersection of the light beam from the beam-limiting device and one of the sets of planes parallel to and including the plane of the image receptor, whose perimeter is the locus of points at which the illumination is one-fourth of the maximum in the intersection."Line-voltage regulation" means the difference between the no-load and the load line potentials expressed as a percent of the load line potential. It is calculated using the following equation: Percent line-voltage regulation = 100 (Vn - V)/V where Vn = No-load line potential and V = Load Line potential."Linear attenuation coefficient" (u) means the quotient of dN/N by dl when dN/N is the fraction of uncharged ionizing radiation that experience interactions in traversing a distance d1 in a specified material."mA" means milliampere."mAs" means milliampere second."Maximum line current" means the root-mean-square current in the supply line of an x-ray system operating at its maximum rating."Mean" (
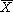 ) means the average value of a set of numbers as set forth in Appendix E."Medical physicist" means an individual having the knowledge and training to measure ionizing radiation, to evaluate safety techniques, and to advise regarding radiation protection needs. For example, "medical physicists" may include individuals certified in the field of diagnostic x-ray systems by the American Board of Radiology in physics, the American Board of Health Physics, the American Board of Medical Physics, individuals licensed by an appropriate state agency, or individuals otherwise deemed by the Department to have equivalent qualifications."MeV" means million electron volts."Minor" means any individual less than 18 years of age."Mobile diagnostic x-ray system" (See definition of "Diagnostic x-ray system" in this Section.)"Multiple tomogram systems" means a computed tomography system, which obtains x-ray transmission data simultaneously during a single scan to produce more than one tomogram."Multiple scan average dose (MSAD)" means the average dose at the center of a series of scans, specified at the center of the axis of rotation of a computed tomography system. MSAD is calculated as set forth in Appendix E."Nominal tomographic section thickness" means the full-width at half-maximum of the sensitivity profile taken at the center of the cross sectional volume over which x-ray transmission data are collected."Noise" means the standard deviation of the fluctuations in CTN expressed as a percentage of the attenuation coefficient of water. Its estimate (Sn) is calculated using the expression set forth in Appendix E."Nominal section thickness" means the fill width at half-maximum of the sensitivity profile taken at the center of the cross-sectional volume over which x-ray transmission data are collected."Occupational dose" means radiation exposure received by an individual in the course of employment in which the individual's duties involve exposure to radiation. Occupational dose shall not include any radiation exposure of an individual for the purpose of diagnosis."Patient" means an individual subjected to healing arts examination or diagnosis."Peak tube potential" (See definition of "kilovolt peak (kVp)" in this Section.)"Permittee" means any person which is issued a permit by the Department in accordance with these regulations and the Act."Person" means any individual, corporation, partnership, firm, association, trust, estate, public or private institution, group, agency, political subdivision of this State, any other State or political subdivision or agency thereof, and any legal successor, representative, agent, or agency of the foregoing."Personnel monitoring equipment" means devices such as film badges, pocket dosimeters, and thermoluminescent dosimeters designed to be worn or carried by an individual for the purpose of estimating the dose received by the individual."Phantom" means a volume of material behaving in a manner similar to tissue with respect to the attenuation and scattering of radiation."Phototimer" means a method for controlling radiation exposures to image receptors by the amount of radiation which reaches a radiation monitoring device(s). The radiation monitoring device(s) is part of an electronic circuit which controls the duration of time the tube is activated. (See definition of "Automatic exposure control" in this Section.)"Physician" means a person who is licensed by either the Oklahoma State Board of Medical Licensure and Supervision or by the Oklahoma State Board of Osteopathic Examiners to practice medicine, radiology, and/or surgery."Picture element" means an elemental area of a tomogram."Portable diagnostic x-ray system" (See definition of "Diagnostic x-ray system" in this Section.)"Practical range of electrons" corresponds to classical electron range where the only contribution to dose is from bremsstrahlung x-rays. Precise definition may be found in ICRU Report 35, "Radiation Dosimetry: Electron Beams with Energies Between 1 and 50 MeV," International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements, September 15, 1984."Primary dose monitoring system" means a system which will monitor the useful beam during irradiation and which will terminate irradiation when a pre-selected number of dose monitor units have been acquired."Primary protective barrier" (See definition of "Protective barrier" in this Section.)"Primary scattered radiation" means that scattered radiation which has been deviated in direction only by materials irradiated by the useful beam. (See also definition of "scattered radiation" in this Section.)"Protective apron" means an apron made of radiation absorbing materials used to reduce radiation exposure."Protective barrier" means a barrier of radiation absorbing material(s) used to reduce radiation exposure. The types of protective barriers are as follows:(A) "Primary protective barrier" means the material, excluding filters, placed in the useful beam, for protection purposes, to reduce the radiation exposure.(B) "Secondary protective barrier" means a barrier sufficient to attenuate the stray radiation to the required degree."Protective glove" means a glove made of radiation absorbing materials used to reduce radiation exposure."Qualified expert" (see definition of "Medical Physicist".)"Rad" means the special unit of absorbed dose. One rad equals 0.01 joule per kilogram (100 ergs per gram) of material; for example; if tissue is the material of interest, then 1 rad equals 0.01 joule per kilogram (0.01 gray) of tissue. (See definition of "Absorbed Dose" in this section.)"Radiation" means ionizing radiation delivered by x rays."Radiation area" means any area, accessible to individuals, in whichradiation levels could result in an individual receiving a dose equivalent in excess of 0.005 rem (0.05 mSv) in 1 hour at 30 centimeters from the radiation source or from any surface that the radiation penetrates."Radiation detector" means a device which, in the presence of radiation, provides a signal or other indication suitable for use in measuring one or more quantities of incident radiation."Radiation head" means the structure from which the useful beam emerges."Radiation machine" means any device capable of producing radiation except those which produce radiation only from radioactive material."Radiation safety officer"(RSO) means one who has been delegated the responsibility to apply all of the appropriate radiation protection regulations."Radioactivity" means the transformation of unstable atomic nuclei by the emission of radiation."Radiograph" means an image receptor on which the image is created directly or indirectly by an x-ray pattern and results in a permanent record."Radiographic imaging system" means any system whereby a permanent or semi-permanent image is recorded on an image receptor by the action of ionizing radiation."Rating" means the operating limits as specified by the component manufacturer."Recording" means producing a permanent form of an image resulting from x-ray photons."Reference plane" means a plane which is displaced from and parallel to the tomographic plane."Registration" means registration with the Department in accordance with this Chapter."Rem" means a special unit of the dose equivalent. One millirem (mrem) = 0.001 rem (See definition of "Dose Equivalent" in this Section.) For the purpose of these regulations, any of the following is considered to be equal to one rem:(A) an exposure of 1 roentgen of x-ray or gamma radiation.(B) an absorbed dose of 1 rad due to x-ray, gamma, or beta radiation.(C) an absorbed dose of 0.05 rad due to particles heavier than protons and with sufficient energy to reach the lens of the eye.(D) an absorbed dose of 0.1 rad due to fast neutrons or high energy protons.(E) an absorbed dose of 0.4 rad due to thermal neutrons.(F) 1 rem = 0.01 sievert."Research and development" means:(A) theoretical analysis, exploration, or experimentation; or(B) the extension of investigative findings and theories of a scientific or technical nature into practical application for experimental and demonstration purposes, including the experimental production and testing of models, devices, equipment, materials, and processes. Research and development does not include the internal or external administration of radiation to human beings."Response time" means the time required for an instrument system to reach 90 percent of its final reading when the radiation-sensitive volume of the instrument system is exposed to a step change in radiation flux from zero sufficient to provide a steady state midscale reading."Restricted area" (controlled area) means any area, access to which is controlled by the permittee for the purpose of protecting individuals from exposure to radiation. A restricted area shall not include any areas used for residential quarters, although a room or rooms in a residential building may be set apart as a restricted area."Roentgen"(R) means the special unit of exposure. One roentgen (R) equals 2.58 x 10-4 coulombs/kilogram of air. (See definition of "Exposure" in this Section.)"Scan" means the complete process of collecting x-ray transmission data for the production of a tomogram. Data can be collected simultaneously during a single scan for the production of one or more tomograms."Scan increment" means the amount of relative displacement of the patient with respect to the CT x-ray system between successive scans measured along the direction of such displacement."Scan sequence" means a preselected set of two or more scans performed consecutively under preselected CT conditions of operation."Scan time" means the periods of time between the beginning and end of x-ray transmission data accumulation for a single scan."Scattered radiation" means radiation that, during passage through matter, has been deviated in direction. (See definition of "Direct scattered radiation" in this Section.)"Secondary dose monitoring system" means a system which will terminate irradiation in the event of failure of the primary system."Secondary protective barrier" (See definition of "Protective barrier" in this Section.)"Shadow tray" means a device attached to the radiation head to support auxiliary beam blocking material."Shallow dose equivalent (SDE)" means the DE at a tissue depth of 0.007 cm (7 mg/cm) averaged over an area of 1 square centimeter (cm). (SDE applies to the external exposure of the skin or an extremity.)"Shutter" means a device attached to the tube housing assembly which can totally intercept the useful beam and which has a lead equivalency not less than that of the tube housing assembly."SI" means the abbreviation for the International System of Units."Single tomogram system" means a CT x-ray system, which obtains x-ray transmission data during a scan to produce a single tomogram."Sievert" (Sv) means the SI unit of any of the qualities expressed as dose equivalent. The dose equivalent in sieverts is equal to the absorbed dose in grays multiplied by the quality factor (1 Sv = 100 rems)."Source" means the focal spot of the x-ray tube."Source-to-image receptor distance (SID)" means the distance from the source to the center of the input surface of the image receptor."Source of radiation" means any instrument capable of producing or emitting radiation. (i.e., x-ray tube assembly.)"Source-to-skin distance (SSD)" means the distance between the source and the skin of the patient."Special procedures" means the application of special x-ray systems and specialized techniques to obtain required diagnostic information. This usually provides enhanced detail of a given anatomical structure but with reduced visualization of other structures. Special procedures include, but are not limited to, angiography, cardiac catheterization, myelography, and surgery."Special purpose x-ray system" means any diagnostic x-ray system, which is limited, by design, to radiographic examinations of specific anatomical regions. Special purpose x-ray systems include, but are not limited to, mammography systems, dedicated chest systems, cystography systems, and head and skull systems."Spot check" means a procedure which is performed to assure that a previous calibration continues to be valid."Spot film" means a radiograph which is made during a fluoroscopic examination to permanently record conditions which exist during that fluoroscopic procedure."Spot-film device" means a device intended to transport and/or position a radiographic image receptor between the x-ray tube head and fluoroscopic image receptor. It includes a device intended to hold a cassette over the input end of an image intensifier for the purpose of making a radiograph ."Standard deviation" (s) means a measure of the dispersion or variation in distribution, equal to the square root of the mean of the squares of the deviations from the mean root of the distribution, as set forth in Appendix E."Stationary diagnostic x-ray system" (See definition of "Diagnostic x-ray system" in this Section.)"Stored system" means a diagnostic x-ray system which has been disabled such that when power is supplied to the control panel (technique indicators), the x-ray tube may not be energized."Stray radiation" means the sum of leakage and scattered radiation."Supervision" means the delegating of the task of applying radiation pursuant to these regulations by persons, not licensed in the healing arts or veterinary medicine, who provide services under the practitioner's control. The licensed practitioner assumes full responsibility for these tasks and must assure that the tasks will be administered correctly."Survey" means an evaluation of the production, use, release, disposal, and/or presence of sources of radiation under a specific set of conditions to determine actual or potential radiation hazards. When appropriate, such evaluation includes, but is not limited to, tests, physical examinations, and measurements of levels of radiation or concentrations of radioactive material present."Target" means that part of a radiation head which by design intercepts a beam of accelerated particles with subsequent emission of other radiation."Technique chart" means a chart that provides all necessary generator control settings and geometry needed to make clinical radiographs when the radiography system is in manual mode."Technique factors" mean the conditions of operation. Technique factor(s) are specified as follows:(A) for capacitor energy storage systems, it is peak tube potential in kV and quantity of charge in mAs;(B) for field emission systems rated for pulsed operation, it is peak tube potential in kV and number of x-ray pulses;(C) for CT systems designed for pulsed operations, it is peak tube potential in kV, scan time in seconds, and either tube current in mA, x-ray pulse width in seconds, and the number of x-ray pulses per scan or the product of tube current, x-ray pulse width, and the number of x-ray pulses in mAs;(D) for CT systems not designed for pulsed operation, it is peak tube potential in kV, and either tube current in mA and scan time in seconds or the product of tube current and exposure time in mAs and the scan time when the scan time and exposure time are equivalent; and(E) for all other systems, it is peak tube potential in kV and either tube current in mA and exposure time in seconds or the product of tube current and exposure time in mAs."Telemedicine" means the use of electronic communication processes for the transmission of information and data related to the diagnosis and/or treatment of medical conditions."Teleradiology" means the electronic transmission of radiological images from one location to another for the purposes of interpretation and/or consultation."Termination of irradiation" means the stopping of irradiation in a fashion which will not permit continuance of irradiation without the resetting of operating conditions at the control panel."Test" means the process of verifying compliance with an applicable regulation."These regulations" means all subchapters of the Diagnostic X-ray Systems Regulations. (Chapter 281 of this Title.)"Tomogram" means the depiction of the x-ray attenuation properties of a section through the body."Tomographic plane" means that geometric plane which is identified as corresponding to the output tomogram."Tomographic section" means the volume of an object whose x-ray attenuation properties are imaged in a tomogram."Total Effective Dose Equivalent (TEDE)" means, for external exposure only to x-ray radiation from diagnostic x-ray systems, the TEDE is equal to the DDE. If an individual receives an occupational dose from both diagnostic x-ray systems and radioactive materials, the TEDE is the sum of the deep-dose equivalent (for external exposures) and the committed effective dose equivalent (for internal exposures)."Traceable to a national standard" means that a quantity or a measurement has been compared to a national standard directly or indirectly through one or more intermediate steps and that all comparisons have been documented."Transfer" means:(A) To change the possession or legal title of a diagnostic x-ray system; or(B) To relocate from one physical address to another."Tube" means an x-ray tube, unless otherwise specified."Tube housing assembly" means the tube housing with tube installed. It includes high-voltage and/or filament transformers and other appropriate elements when such are contained within the tube housing."Tube rating chart" means the set of curves which specify the rated limits of operation of the tube in terms of the technique factors."Unrestricted area" (uncontrolled area) means any area access which is not controlled by the permittee for purposes of protection of individuals from exposure to radiation and any area used for residential quarters."Useful beam" means the radiation emanating from the tube housing port or the radiation head and passing through the aperture of the beam limiting service when the exposure controls are in a mode to cause the system to produce radiation."User" means any person who causes any radiation producing machine, subject to these regulations, to be energized."Variable-aperture beam-limiting device" means a beam-limiting device which has capacity for stepless adjustment of the x-ray field size at a given SID."Virtual source" means a point from which radiation appears to originate."Visible area" means that portion of the input surface of the image receptor over which incident x-ray photons produce a visible image."Wedge filter" means an added filter effecting continuous progressive attenuation on all or part of the useful beam."Whole Body" means for purposes of external exposure, head, trunk (including male gonads), arms above the elbow, or legs above the knee."Worker" means an individual engaged in work in a facility issued a permit by the Department and controlled by a permittee, but does not include the permittee."X-ray control" means a device which controls input power to the x-ray high-voltage generator or the x-ray tube. It includes equipment such as timers, phototimers, automatic brightness stabilizers, and similar devices which control the technique factors of an x-ray exposure."X-ray field" means that area of the intersection of the useful beam and any one of the set of planes parallel to and including the plane of the image receptor whose perimeter is the locus of points at which the exposure rate is one-fourth of the maximum in the intersection."X-ray high-voltage generator" means a device which transforms electrical energy from the potential supplied by the x-ray control to the tube operating potential. The device may also include means for transforming alternating current to direct current, filament transformers for the x-ray tube(s), high-voltage switches, electrical protective devices, and other appropriate elements."X-ray subsystem" means any combination of two or more components of an x-ray system."X-ray system" means an assemblage of components for the controlled production of x-rays. It includes minimally an x-ray high-voltage generator, an x-ray control, a tube housing assembly, a beam-limiting device, and the necessary supporting structures. Additional components which function with the system are considered integral parts of the system."X-ray tube" means any electron tube which is designed to be used primarily for the production of x-rays.
) means the average value of a set of numbers as set forth in Appendix E."Medical physicist" means an individual having the knowledge and training to measure ionizing radiation, to evaluate safety techniques, and to advise regarding radiation protection needs. For example, "medical physicists" may include individuals certified in the field of diagnostic x-ray systems by the American Board of Radiology in physics, the American Board of Health Physics, the American Board of Medical Physics, individuals licensed by an appropriate state agency, or individuals otherwise deemed by the Department to have equivalent qualifications."MeV" means million electron volts."Minor" means any individual less than 18 years of age."Mobile diagnostic x-ray system" (See definition of "Diagnostic x-ray system" in this Section.)"Multiple tomogram systems" means a computed tomography system, which obtains x-ray transmission data simultaneously during a single scan to produce more than one tomogram."Multiple scan average dose (MSAD)" means the average dose at the center of a series of scans, specified at the center of the axis of rotation of a computed tomography system. MSAD is calculated as set forth in Appendix E."Nominal tomographic section thickness" means the full-width at half-maximum of the sensitivity profile taken at the center of the cross sectional volume over which x-ray transmission data are collected."Noise" means the standard deviation of the fluctuations in CTN expressed as a percentage of the attenuation coefficient of water. Its estimate (Sn) is calculated using the expression set forth in Appendix E."Nominal section thickness" means the fill width at half-maximum of the sensitivity profile taken at the center of the cross-sectional volume over which x-ray transmission data are collected."Occupational dose" means radiation exposure received by an individual in the course of employment in which the individual's duties involve exposure to radiation. Occupational dose shall not include any radiation exposure of an individual for the purpose of diagnosis."Patient" means an individual subjected to healing arts examination or diagnosis."Peak tube potential" (See definition of "kilovolt peak (kVp)" in this Section.)"Permittee" means any person which is issued a permit by the Department in accordance with these regulations and the Act."Person" means any individual, corporation, partnership, firm, association, trust, estate, public or private institution, group, agency, political subdivision of this State, any other State or political subdivision or agency thereof, and any legal successor, representative, agent, or agency of the foregoing."Personnel monitoring equipment" means devices such as film badges, pocket dosimeters, and thermoluminescent dosimeters designed to be worn or carried by an individual for the purpose of estimating the dose received by the individual."Phantom" means a volume of material behaving in a manner similar to tissue with respect to the attenuation and scattering of radiation."Phototimer" means a method for controlling radiation exposures to image receptors by the amount of radiation which reaches a radiation monitoring device(s). The radiation monitoring device(s) is part of an electronic circuit which controls the duration of time the tube is activated. (See definition of "Automatic exposure control" in this Section.)"Physician" means a person who is licensed by either the Oklahoma State Board of Medical Licensure and Supervision or by the Oklahoma State Board of Osteopathic Examiners to practice medicine, radiology, and/or surgery."Picture element" means an elemental area of a tomogram."Portable diagnostic x-ray system" (See definition of "Diagnostic x-ray system" in this Section.)"Practical range of electrons" corresponds to classical electron range where the only contribution to dose is from bremsstrahlung x-rays. Precise definition may be found in ICRU Report 35, "Radiation Dosimetry: Electron Beams with Energies Between 1 and 50 MeV," International Commission on Radiation Units and Measurements, September 15, 1984."Primary dose monitoring system" means a system which will monitor the useful beam during irradiation and which will terminate irradiation when a pre-selected number of dose monitor units have been acquired."Primary protective barrier" (See definition of "Protective barrier" in this Section.)"Primary scattered radiation" means that scattered radiation which has been deviated in direction only by materials irradiated by the useful beam. (See also definition of "scattered radiation" in this Section.)"Protective apron" means an apron made of radiation absorbing materials used to reduce radiation exposure."Protective barrier" means a barrier of radiation absorbing material(s) used to reduce radiation exposure. The types of protective barriers are as follows:(A) "Primary protective barrier" means the material, excluding filters, placed in the useful beam, for protection purposes, to reduce the radiation exposure.(B) "Secondary protective barrier" means a barrier sufficient to attenuate the stray radiation to the required degree."Protective glove" means a glove made of radiation absorbing materials used to reduce radiation exposure."Qualified expert" (see definition of "Medical Physicist".)"Rad" means the special unit of absorbed dose. One rad equals 0.01 joule per kilogram (100 ergs per gram) of material; for example; if tissue is the material of interest, then 1 rad equals 0.01 joule per kilogram (0.01 gray) of tissue. (See definition of "Absorbed Dose" in this section.)"Radiation" means ionizing radiation delivered by x rays."Radiation area" means any area, accessible to individuals, in whichradiation levels could result in an individual receiving a dose equivalent in excess of 0.005 rem (0.05 mSv) in 1 hour at 30 centimeters from the radiation source or from any surface that the radiation penetrates."Radiation detector" means a device which, in the presence of radiation, provides a signal or other indication suitable for use in measuring one or more quantities of incident radiation."Radiation head" means the structure from which the useful beam emerges."Radiation machine" means any device capable of producing radiation except those which produce radiation only from radioactive material."Radiation safety officer"(RSO) means one who has been delegated the responsibility to apply all of the appropriate radiation protection regulations."Radioactivity" means the transformation of unstable atomic nuclei by the emission of radiation."Radiograph" means an image receptor on which the image is created directly or indirectly by an x-ray pattern and results in a permanent record."Radiographic imaging system" means any system whereby a permanent or semi-permanent image is recorded on an image receptor by the action of ionizing radiation."Rating" means the operating limits as specified by the component manufacturer."Recording" means producing a permanent form of an image resulting from x-ray photons."Reference plane" means a plane which is displaced from and parallel to the tomographic plane."Registration" means registration with the Department in accordance with this Chapter."Rem" means a special unit of the dose equivalent. One millirem (mrem) = 0.001 rem (See definition of "Dose Equivalent" in this Section.) For the purpose of these regulations, any of the following is considered to be equal to one rem:(A) an exposure of 1 roentgen of x-ray or gamma radiation.(B) an absorbed dose of 1 rad due to x-ray, gamma, or beta radiation.(C) an absorbed dose of 0.05 rad due to particles heavier than protons and with sufficient energy to reach the lens of the eye.(D) an absorbed dose of 0.1 rad due to fast neutrons or high energy protons.(E) an absorbed dose of 0.4 rad due to thermal neutrons.(F) 1 rem = 0.01 sievert."Research and development" means:(A) theoretical analysis, exploration, or experimentation; or(B) the extension of investigative findings and theories of a scientific or technical nature into practical application for experimental and demonstration purposes, including the experimental production and testing of models, devices, equipment, materials, and processes. Research and development does not include the internal or external administration of radiation to human beings."Response time" means the time required for an instrument system to reach 90 percent of its final reading when the radiation-sensitive volume of the instrument system is exposed to a step change in radiation flux from zero sufficient to provide a steady state midscale reading."Restricted area" (controlled area) means any area, access to which is controlled by the permittee for the purpose of protecting individuals from exposure to radiation. A restricted area shall not include any areas used for residential quarters, although a room or rooms in a residential building may be set apart as a restricted area."Roentgen"(R) means the special unit of exposure. One roentgen (R) equals 2.58 x 10-4 coulombs/kilogram of air. (See definition of "Exposure" in this Section.)"Scan" means the complete process of collecting x-ray transmission data for the production of a tomogram. Data can be collected simultaneously during a single scan for the production of one or more tomograms."Scan increment" means the amount of relative displacement of the patient with respect to the CT x-ray system between successive scans measured along the direction of such displacement."Scan sequence" means a preselected set of two or more scans performed consecutively under preselected CT conditions of operation."Scan time" means the periods of time between the beginning and end of x-ray transmission data accumulation for a single scan."Scattered radiation" means radiation that, during passage through matter, has been deviated in direction. (See definition of "Direct scattered radiation" in this Section.)"Secondary dose monitoring system" means a system which will terminate irradiation in the event of failure of the primary system."Secondary protective barrier" (See definition of "Protective barrier" in this Section.)"Shadow tray" means a device attached to the radiation head to support auxiliary beam blocking material."Shallow dose equivalent (SDE)" means the DE at a tissue depth of 0.007 cm (7 mg/cm) averaged over an area of 1 square centimeter (cm). (SDE applies to the external exposure of the skin or an extremity.)"Shutter" means a device attached to the tube housing assembly which can totally intercept the useful beam and which has a lead equivalency not less than that of the tube housing assembly."SI" means the abbreviation for the International System of Units."Single tomogram system" means a CT x-ray system, which obtains x-ray transmission data during a scan to produce a single tomogram."Sievert" (Sv) means the SI unit of any of the qualities expressed as dose equivalent. The dose equivalent in sieverts is equal to the absorbed dose in grays multiplied by the quality factor (1 Sv = 100 rems)."Source" means the focal spot of the x-ray tube."Source-to-image receptor distance (SID)" means the distance from the source to the center of the input surface of the image receptor."Source of radiation" means any instrument capable of producing or emitting radiation. (i.e., x-ray tube assembly.)"Source-to-skin distance (SSD)" means the distance between the source and the skin of the patient."Special procedures" means the application of special x-ray systems and specialized techniques to obtain required diagnostic information. This usually provides enhanced detail of a given anatomical structure but with reduced visualization of other structures. Special procedures include, but are not limited to, angiography, cardiac catheterization, myelography, and surgery."Special purpose x-ray system" means any diagnostic x-ray system, which is limited, by design, to radiographic examinations of specific anatomical regions. Special purpose x-ray systems include, but are not limited to, mammography systems, dedicated chest systems, cystography systems, and head and skull systems."Spot check" means a procedure which is performed to assure that a previous calibration continues to be valid."Spot film" means a radiograph which is made during a fluoroscopic examination to permanently record conditions which exist during that fluoroscopic procedure."Spot-film device" means a device intended to transport and/or position a radiographic image receptor between the x-ray tube head and fluoroscopic image receptor. It includes a device intended to hold a cassette over the input end of an image intensifier for the purpose of making a radiograph ."Standard deviation" (s) means a measure of the dispersion or variation in distribution, equal to the square root of the mean of the squares of the deviations from the mean root of the distribution, as set forth in Appendix E."Stationary diagnostic x-ray system" (See definition of "Diagnostic x-ray system" in this Section.)"Stored system" means a diagnostic x-ray system which has been disabled such that when power is supplied to the control panel (technique indicators), the x-ray tube may not be energized."Stray radiation" means the sum of leakage and scattered radiation."Supervision" means the delegating of the task of applying radiation pursuant to these regulations by persons, not licensed in the healing arts or veterinary medicine, who provide services under the practitioner's control. The licensed practitioner assumes full responsibility for these tasks and must assure that the tasks will be administered correctly."Survey" means an evaluation of the production, use, release, disposal, and/or presence of sources of radiation under a specific set of conditions to determine actual or potential radiation hazards. When appropriate, such evaluation includes, but is not limited to, tests, physical examinations, and measurements of levels of radiation or concentrations of radioactive material present."Target" means that part of a radiation head which by design intercepts a beam of accelerated particles with subsequent emission of other radiation."Technique chart" means a chart that provides all necessary generator control settings and geometry needed to make clinical radiographs when the radiography system is in manual mode."Technique factors" mean the conditions of operation. Technique factor(s) are specified as follows:(A) for capacitor energy storage systems, it is peak tube potential in kV and quantity of charge in mAs;(B) for field emission systems rated for pulsed operation, it is peak tube potential in kV and number of x-ray pulses;(C) for CT systems designed for pulsed operations, it is peak tube potential in kV, scan time in seconds, and either tube current in mA, x-ray pulse width in seconds, and the number of x-ray pulses per scan or the product of tube current, x-ray pulse width, and the number of x-ray pulses in mAs;(D) for CT systems not designed for pulsed operation, it is peak tube potential in kV, and either tube current in mA and scan time in seconds or the product of tube current and exposure time in mAs and the scan time when the scan time and exposure time are equivalent; and(E) for all other systems, it is peak tube potential in kV and either tube current in mA and exposure time in seconds or the product of tube current and exposure time in mAs."Telemedicine" means the use of electronic communication processes for the transmission of information and data related to the diagnosis and/or treatment of medical conditions."Teleradiology" means the electronic transmission of radiological images from one location to another for the purposes of interpretation and/or consultation."Termination of irradiation" means the stopping of irradiation in a fashion which will not permit continuance of irradiation without the resetting of operating conditions at the control panel."Test" means the process of verifying compliance with an applicable regulation."These regulations" means all subchapters of the Diagnostic X-ray Systems Regulations. (Chapter 281 of this Title.)"Tomogram" means the depiction of the x-ray attenuation properties of a section through the body."Tomographic plane" means that geometric plane which is identified as corresponding to the output tomogram."Tomographic section" means the volume of an object whose x-ray attenuation properties are imaged in a tomogram."Total Effective Dose Equivalent (TEDE)" means, for external exposure only to x-ray radiation from diagnostic x-ray systems, the TEDE is equal to the DDE. If an individual receives an occupational dose from both diagnostic x-ray systems and radioactive materials, the TEDE is the sum of the deep-dose equivalent (for external exposures) and the committed effective dose equivalent (for internal exposures)."Traceable to a national standard" means that a quantity or a measurement has been compared to a national standard directly or indirectly through one or more intermediate steps and that all comparisons have been documented."Transfer" means:(A) To change the possession or legal title of a diagnostic x-ray system; or(B) To relocate from one physical address to another."Tube" means an x-ray tube, unless otherwise specified."Tube housing assembly" means the tube housing with tube installed. It includes high-voltage and/or filament transformers and other appropriate elements when such are contained within the tube housing."Tube rating chart" means the set of curves which specify the rated limits of operation of the tube in terms of the technique factors."Unrestricted area" (uncontrolled area) means any area access which is not controlled by the permittee for purposes of protection of individuals from exposure to radiation and any area used for residential quarters."Useful beam" means the radiation emanating from the tube housing port or the radiation head and passing through the aperture of the beam limiting service when the exposure controls are in a mode to cause the system to produce radiation."User" means any person who causes any radiation producing machine, subject to these regulations, to be energized."Variable-aperture beam-limiting device" means a beam-limiting device which has capacity for stepless adjustment of the x-ray field size at a given SID."Virtual source" means a point from which radiation appears to originate."Visible area" means that portion of the input surface of the image receptor over which incident x-ray photons produce a visible image."Wedge filter" means an added filter effecting continuous progressive attenuation on all or part of the useful beam."Whole Body" means for purposes of external exposure, head, trunk (including male gonads), arms above the elbow, or legs above the knee."Worker" means an individual engaged in work in a facility issued a permit by the Department and controlled by a permittee, but does not include the permittee."X-ray control" means a device which controls input power to the x-ray high-voltage generator or the x-ray tube. It includes equipment such as timers, phototimers, automatic brightness stabilizers, and similar devices which control the technique factors of an x-ray exposure."X-ray field" means that area of the intersection of the useful beam and any one of the set of planes parallel to and including the plane of the image receptor whose perimeter is the locus of points at which the exposure rate is one-fourth of the maximum in the intersection."X-ray high-voltage generator" means a device which transforms electrical energy from the potential supplied by the x-ray control to the tube operating potential. The device may also include means for transforming alternating current to direct current, filament transformers for the x-ray tube(s), high-voltage switches, electrical protective devices, and other appropriate elements."X-ray subsystem" means any combination of two or more components of an x-ray system."X-ray system" means an assemblage of components for the controlled production of x-rays. It includes minimally an x-ray high-voltage generator, an x-ray control, a tube housing assembly, a beam-limiting device, and the necessary supporting structures. Additional components which function with the system are considered integral parts of the system."X-ray tube" means any electron tube which is designed to be used primarily for the production of x-rays.